 Language
▼
Language
▼
More Language
Galvanized sheet metal,commonly referred to as galvanized sheet,is mainly made by coating a layer of metallic zinc on the surface of steel or iron plates.This galvanized layer is formed on the surface of the steel plate through a series of production processes,with the main purpose of enhancing the corrosion resistance of the steel plate.The following is a detailed introduction to the material of galvanized sheet metal:
The main materials of galvanized sheet metal are steel plate(or iron plate)and metallic zinc.Steel plate,as the substrate,provides sufficient strength and hardness,while metallic zinc serves as the coating,mainly playing a role in corrosion prevention.
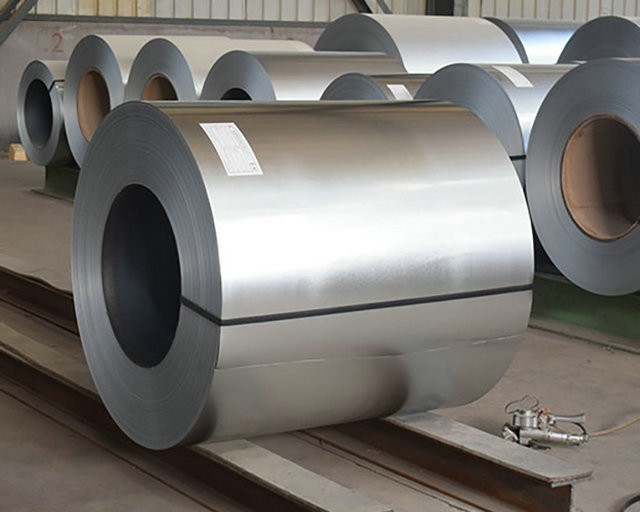

The production process mainly includes steps such as raw material preparation,acid washing,cold rolling,hot-dip galvanizing,post-treatment,cooling and straightening,cutting,and packaging.Among them,hot-dip galvanizing is the core process,which determines the thickness and quality of the galvanized layer on the galvanized sheet metal.In this step,the steel plate enters the molten zinc solution and undergoes a chemical reaction between zinc and the steel plate through immersion plating,forming an alloy layer of zinc and steel.
China galvanized plate manufacturer: Boxing Shuangshengda Steel specializes in galvanized sheet, galvanized steel plate,Colour steel plate etc.We have a full range of product specifications and types, low prices, and more than 20 years of experience, worthy of your trust